Author Finder helps you to find variants of the same author name or to distinguish one author from another by field of research and/or address.
Author names are in the form: last name followed by up to five initials.
![]() You access
Author Finder by clicking the Author Finder link that appears under the
Author field on the default Search page.
You access
Author Finder by clicking the Author Finder link that appears under the
Author field on the default Search page.
Step 1: Enter Author Name
Enter the last name of the author in the Last Name box. A last name can contain a hyphen, a space, or an apostrophe. These are all valid entries:
- Wilson
- O'Grady
- OGrady
- Van der Waals
- Ruiz-Gomez
- RuizGomez
You must enter a full last name. A partial or truncated name will not match full names in Author Finder. For example, if you enter Rothsch or Rothsch*, you will not retrieve Rothschild.
You may click Next to retrieve a list of all author names that match your entry, or you may enter one or more initials. Keep in mind that the more initials you enter, the more restrictive your search.
Step 2: Select Author Variant
Scan the list of author names that match your entry in step 1. The exact name you entered is at the top of the list, and it is selected by default. You may click Next to use this author name in your product search, or you may select another name from the list.
All of the other names are followed by an asterisk. The asterisk stands for any additional initials or no additional initials. Consider this example:
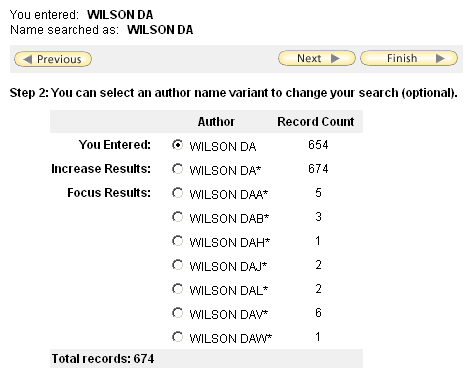
The record count for Wilson DA is 654, but the record count for Wilson DA* is 674. In a search query, Wilson DA* will retrieve records containing the names:
- Wilson DA
- Wilson DAA
- Wilson DAB
- Wilson DAH
- and so on
This is why selecting Wilson DA* will increase your results. The other names on the list will focus your results, since they are narrower variants on the name Wilson DA.
Record Count is the total number of records in Web of Science that contain the name. This total is the total for all years of Web of Science, and not the years you selected at the start of your search.
Select an author name from the list, and then click Next, or click Add Another Name to look for more variants.
Step 3: Select Subject Category (optional)
To help narrow your author search, you may find it helpful to select a subject category. Six broad subject categories are available plus an All subjects category.
For example, to distinguish the social scientist Johnson RJ from other researchers named Johnson RJ, select Social Sciences.
The Record Count column shows the number of records assigned to each subject category. This number may be higher than the actual number of records containing the author name you selected. Subject categories in Author Finder are very broad; one record may be counted more than once because it has been assigned to multiple subcategories. For example, a record assigned to both Business and Political Science will be counted twice as a Social Sciences record.
Step 4: Select Institution (optional)
Another way to narrow your author search is to select one or more institutions. The institutions you see are all of the institutions in the Address field in records for the author name you selected.
For example, if you are interested in the work of the chemist Thomas Ziegler at the University of Calgary and not the work of Thomas Ziegler at Emory University or Thomas Ziegler at Princeton University, you would select Univ Calgary from the list.
About Author Names
Different authors may be represented by the same name in Web of Science. For example, the authors Richard J. Johnson and Robert J. Johnson are both indexed in Web of Science as Johnson RJ.
Conversely, the same author may be represented by different names, particularly if he or she has a long publication history. For example, Barbara Demmig-Adams is indexed as:
- Demmig-Adams B
- DemmigAdams B
- Demmig B
Search History
The results of your Author Finder search will appear as a set in your search history. You may combine this set with any other sets to create a new search.
Information About ...